Decentralized finance (DeFi) has emerged as a disruptive force in the traditional financial landscape, leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts to create a more transparent, accessible, and efficient financial ecosystem. Smart contract platforms are at the forefront of this revolution, enabling the development of decentralized applications (dApps) that facilitate various financial services without the need for intermediaries. These platforms provide a decentralized infrastructure for executing self-enforcing digital contracts, allowing for the creation of innovative financial products and services that challenge the status quo.
This article aims to explore five prominent smart contract platforms that are disrupting traditional finance, highlighting their unique features, use cases, and potential impact on the industry. By understanding the capabilities and strengths of these platforms, we can gain insights into the transformative power of DeFi and its potential to reshape the financial landscape.
Ethereum
As the pioneering smart contract platform, Ethereum has paved the way for the development of numerous DeFi applications. Launched in 2015, Ethereum introduced the concept of a decentralized virtual machine, known as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which executes smart contracts written in the Solidity programming language. This groundbreaking innovation has enabled the creation of decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, stablecoins, and a wide range of other DeFi applications.
Ethereum’s robust ecosystem and active developer community have contributed to its dominance in the DeFi space. The platform’s smart contract capabilities have facilitated the creation of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which operate based on predefined rules encoded in smart contracts, eliminating the need for centralized governance. Additionally, Ethereum’s support for tokenization has enabled the creation of various digital assets, including non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which have found applications in areas such as digital art, gaming, and collectibles.
Despite its pioneering role, Ethereum has faced challenges in terms of scalability and high transaction fees, particularly during periods of high network congestion. To address these issues, the Ethereum community is actively working on upgrades, such as the transition to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism and the implementation of sharding, which aims to improve the platform’s scalability and efficiency.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Developed by the leading cryptocurrency exchange Binance, BSC is a high-performance blockchain designed specifically for DeFi applications. Recognizing the limitations of Ethereum’s scalability and high transaction fees, Binance aimed to create a more efficient and cost-effective alternative for the DeFi ecosystem.
BSC is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to easily port their existing Ethereum-based dApps and smart contracts to the BSC network. However, BSC employs a more efficient consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Staked-Authority (PoSA), which combines elements of Proof-of-Authority (PoA) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS). This hybrid approach enables faster transaction times and lower fees compared to Ethereum, making it an attractive option for developers and users alike.
One of the key advantages of BSC is its integration with the Binance ecosystem, which includes the popular Binance DEX (decentralized exchange) and the Binance Chain. This integration allows for seamless interoperability between the BSC network and other Binance products, facilitating the development of cross-chain applications and enhancing the overall user experience.
BSC has gained significant traction in the DeFi space, with numerous projects leveraging its capabilities. Popular DeFi applications built on BSC include decentralized exchanges like PancakeSwap, lending platforms like Venus, and yield farming protocols like BakerySwap. The lower transaction fees and faster confirmation times have made BSC an appealing choice for users seeking cost-effective and efficient DeFi solutions.
Solana
Solana is a high-speed, low-cost blockchain that has gained popularity for its scalability and energy efficiency. Developed with the goal of addressing the limitations of existing blockchain platforms, Solana aims to provide a robust infrastructure for decentralized applications, particularly those in the DeFi space.
At the core of Solana’s architecture is its unique Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus mechanism, which is a variation of the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. PoH enables the creation of a historical record that cryptographically verifies the order and passage of time between events, allowing for more efficient processing of transactions. This innovative approach, combined with other optimizations such as Sealevel parallelism and Turbine block propagation, enables Solana to process thousands of transactions per second, making it well-suited for DeFi applications that require high throughput.
In addition to its impressive scalability, Solana is also known for its energy efficiency. Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, which rely on energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, Solana’s PoH and PoS hybrid approach significantly reduces the energy consumption associated with validating transactions and securing the network.
Solana has attracted a growing ecosystem of DeFi projects, including decentralized exchanges like Serum and Raydium, lending platforms like Solend, and yield farming protocols like Quarry. The platform’s high throughput and low transaction fees have made it an attractive choice for developers seeking to build high-performance DeFi applications.
Furthermore, Solana’s focus on user experience and developer-friendly tools has contributed to its growing popularity. The platform offers a robust development environment, including the Rust-based Solana Programming Model and the Solana Web3.js library, which simplifies the process of building and deploying decentralized applications on the network.
Avalanche
Avalanche is a highly scalable and interoperable blockchain platform that aims to address the limitations of previous generations. Developed by Ava Labs, Avalanche employs a novel consensus protocol called Avalanche Consensus, which combines the benefits of classical consensus protocols with the scalability of modern networking techniques.
One of the key features of Avalanche is its support for Ethereum-compatible smart contracts, allowing developers to easily port their existing Ethereum-based dApps and smart contracts to the Avalanche network. This compatibility has made Avalanche an attractive choice for DeFi developers seeking a more scalable and efficient platform.
Avalanche’s architecture is designed to be highly scalable, with the ability to process thousands of transactions per second. It achieves this by partitioning the network into multiple subnetworks, each responsible for processing a specific set of transactions. This approach enables parallel processing and reduces the overall load on the network, resulting in improved performance and throughput.
In addition to its scalability, Avalanche also prioritizes interoperability. The platform supports the creation of customized blockchains, called subnets, which can interact with the main Avalanche network and other subnets. This feature enables the development of cross-chain applications and facilitates the transfer of assets and data between different blockchain ecosystems.
Avalanche hosts a diverse range of DeFi applications, including decentralized exchanges like Trader Joe, lending protocols like Benqi, and stablecoins like AVAX USD. The platform’s high throughput, low transaction fees, and Ethereum compatibility have made it an appealing choice for developers seeking to build high-performance DeFi solutions.
Polkadot
Polkadot is a multi-chain network that enables interoperability between different blockchains, including those designed for DeFi applications. Developed by the Web3 Foundation, Polkadot aims to solve the scalability and interoperability challenges faced by existing blockchain platforms.
At the core of Polkadot’s architecture is the Relay Chain, which acts as a central hub for connecting and coordinating various specialized blockchains called “parachains.” These parachains can be customized to serve specific purposes, such as DeFi applications, gaming platforms, or supply chain management systems.
Polkadot’s unique architecture allows for the creation of customized parachains that can interact with the main Polkadot relay chain, facilitating cross-chain communication and asset transfers. This interoperability enables the seamless exchange of data and value between different blockchain ecosystems, unlocking new possibilities for decentralized applications and services.
In the DeFi space, Polkadot’s ecosystem is rapidly expanding, with various projects leveraging its capabilities. For example, Acala Network is a DeFi hub built on Polkadot, offering a suite of financial products and services, including a decentralized stablecoin, a trustless staking derivative, and a multi-collateral backed loan platform.
Polkadot’s focus on scalability, interoperability, and governance has made it an attractive choice for developers seeking to build decentralized applications that can seamlessly interact with other blockchain networks. The platform’s robust developer tools and active community contribute to its growing adoption in the DeFi ecosystem.
Charting the Rise of Smart Contract Platforms
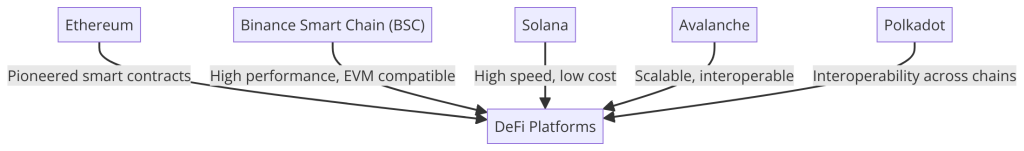
The digital finance landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, propelled by the advent of smart contract platforms that challenge the traditional financial paradigms. “The Vanguard of Finance,” our graphically represented diagram, encapsulates the essence of this revolution, showcasing five pivotal platforms that are at the helm of the DeFi movement.
At the core of this transformation is Ethereum, the trailblazer that introduced the world to the potential of smart contracts. Surrounding Ethereum in our visual representation are Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Solana, Avalanche, and Polkadot, each contributing unique advancements and solutions to the challenges of scalability, interoperability, and cost-efficiency.
This diagram vividly illustrates the interconnectedness of these platforms with the broader DeFi ecosystem, highlighting their roles in pioneering a new era of decentralized applications. From fostering rapid, cost-effective transactions on Solana to enabling cross-chain operability on Polkadot, each platform brings distinct capabilities that together weave the fabric of a new financial infrastructure.
“The Vanguard of Finance” not only serves as a visual testament to the innovation these platforms represent but also as a beacon for those navigating the burgeoning world of decentralized finance. It reflects the synergistic potential of these platforms to reshape our financial systems, making them more inclusive, efficient, and transparent.
What Are Some Examples Of Defi Applications Built On Avalanche
Here are some examples of DeFi applications built on the Avalanche blockchain:
- Aave – A decentralized lending and borrowing platform that allows users to earn interest on their crypto assets or take out loans using their assets as collateral.
- 1inch – A decentralized exchange (DEX) aggregator that sources liquidity from multiple DEXs to provide the best prices for token swaps.
- GMX – A decentralized spot and perpetual futures exchange that allows traders to go long or short on various crypto assets with leverage.
- Matcha – Another DEX aggregator that combines liquidity from multiple sources to offer the best token swap rates.
- Yield Yak – A yield optimization platform that helps users maximize their returns by automatically routing assets to the highest-yielding DeFi protocols.
- PoolTogether – A no-loss lottery platform where users can deposit their assets into a prize pool and earn interest while also having a chance to win the entire pool.
- Iron Bank – A decentralized banking platform that offers services like lending, borrowing, and interest-earning accounts.
- FutureSwap – A decentralized futures exchange that allows traders to speculate on the future prices of various crypto assets.
- DeBank – A DeFi portfolio management and analytics platform that helps users track their DeFi investments across multiple protocols.
- Dexalot – A decentralized exchange that facilitates trading of various crypto assets and derivatives.
- Benqi – A decentralized lending protocol that allows users to lend, borrow, and earn interest on their crypto assets.
- Trader Joe – A decentralized exchange that offers trading of various tokens and liquidity pools for yield farming.
What Are The Most Popular Defi Applications Built On Avalanche
Here are some of the most popular and prominent DeFi applications built on the Avalanche blockchain:
- Aave – A leading decentralized lending and borrowing protocol that has launched its V3 version on Avalanche, allowing users to lend and borrow various crypto assets.
- Trader Joe – One of the top decentralized exchanges (DEXs) on Avalanche, facilitating trading of various tokens and providing liquidity pools for yield farming.
- Benqi – A popular lending and liquid staking protocol on Avalanche, enabling users to lend, borrow, and earn interest on their crypto assets.
- GMX – A decentralized spot and perpetual futures trading platform that offers low swap fees and up to 50x leverage.
- Pangolin – A DEX on Avalanche that supports swapping of various tokens and provides liquidity pools for yield farming.
- SushiSwap – The popular Ethereum-based DEX has also launched on Avalanche, allowing users to swap tokens and participate in liquidity pools.
- TrueUSD – A stablecoin project that has integrated with Avalanche, enabling the use of its USD-pegged stablecoin on the platform.
- 1inch – A DEX aggregator that sources liquidity from multiple DEXs, including those on Avalanche, to provide the best token swap rates.
- Matcha – Another DEX aggregator operating on Avalanche, combining liquidity from various sources for optimized token swaps.
- Yield Yak – A yield optimization platform that helps users maximize their returns by automatically routing assets to the highest-yielding DeFi protocols on Avalanche.
These applications cover a wide range of DeFi services, including lending, borrowing, trading, yield farming, and stablecoins, showcasing the diverse ecosystem built on the Avalanche blockchain.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Avalanche For Defi Applications Compared To Other Blockchain Platforms
Here are some key benefits of using Avalanche for building decentralized finance (DeFi) applications compared to other blockchain platforms:
1. High scalability and throughput:
– Avalanche can process over 4,500 transactions per second, making it one of the fastest blockchains.
– It achieves high scalability through its novel consensus protocol (Avalanche Consensus) and the use of multiple sub-networks (subnets) that enable parallel processing.
– This high throughput makes Avalanche well-suited for DeFi applications that require high transaction volumes and low latency.
2. Low transaction fees:
– Avalanche offers low transaction fees, even during periods of high network activity, thanks to its scalable architecture.
– This cost-effectiveness makes Avalanche an attractive option for users seeking affordable blockchain solutions, especially for DeFi applications that involve frequent transactions.
3. Fast transaction finality:
– Avalanche can finalize transactions in less than a second, providing near-instant transaction confirmation.
– This fast finality is crucial for DeFi applications that require real-time settlement, such as decentralized exchanges and lending platforms.
4. Ethereum compatibility:
– Avalanche supports the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Ethereum’s developer toolkit, allowing easy migration of existing Ethereum-based DeFi applications.
– This compatibility enables developers to leverage Avalanche’s scalability and speed while still utilizing familiar tools and languages.
5. Interoperability and cross-chain communication:
– Avalanche’s architecture facilitates interoperability between different blockchain networks, enabling cross-chain asset transfers and communication.
– This feature allows DeFi applications built on Avalanche to interact with other blockchain ecosystems, increasing their utility and accessibility.
6. Customizable subnets:
– Avalanche allows the creation of customized subnets (sub-networks) with their own set of rules and validators.
– This flexibility enables developers to build tailored DeFi solutions for specific use cases or enterprise requirements.
7. Growing ecosystem and adoption:
– Avalanche has attracted a growing ecosystem of DeFi projects, including decentralized exchanges (e.g., Trader Joe, Pangolin), lending platforms (e.g., Benqi, Aave), and stablecoins (e.g., AVAX USD).
– The increasing adoption and investment in the Avalanche ecosystem contribute to its long-term sustainability and potential for innovation in the DeFi space.
While Avalanche offers several advantages for DeFi applications, it’s important to note that other blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain, also have their strengths and established ecosystems. The choice of platform ultimately depends on the specific requirements and priorities of the DeFi project, such as scalability, cost, interoperability, and developer familiarity.
In Conclusion
The rise of smart contract platforms has catalyzed the growth of DeFi, offering innovative solutions that challenge traditional financial services. Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Avalanche, and Polkadot are at the forefront of this disruption, each offering unique features and capabilities that cater to the diverse needs of the DeFi ecosystem. As the adoption of DeFi continues to grow, these platforms will play a crucial role in shaping the future of finance, enabling greater accessibility, transparency, and financial inclusion. However, it is essential to address the challenges and risks associated with DeFi, such as regulatory uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and scalability issues, to ensure its long-term sustainability and widespread adoption.

Cassandra Toroian is a sports-tech entrepreneur and CEO/co-founder of Ruley, the AI “e-referee” serving tennis, pickleball, padel, golf, and soccer. With 25+ years building companies—and a background in finance (MBA) plus Python training—she’s also co-founder of Volleybird and author of Don’t Buy the Bull. A former Division I tennis player, she’s focused on using AI to make sport fairer and more accessible.

